Related questions:
– Briefly describe the architecture of a Recurrent Neural Network (RNN)
– What is Long-Short Term Memory (LSTM)?
– What are transformers? Discuss the major breakthroughs in transformer models
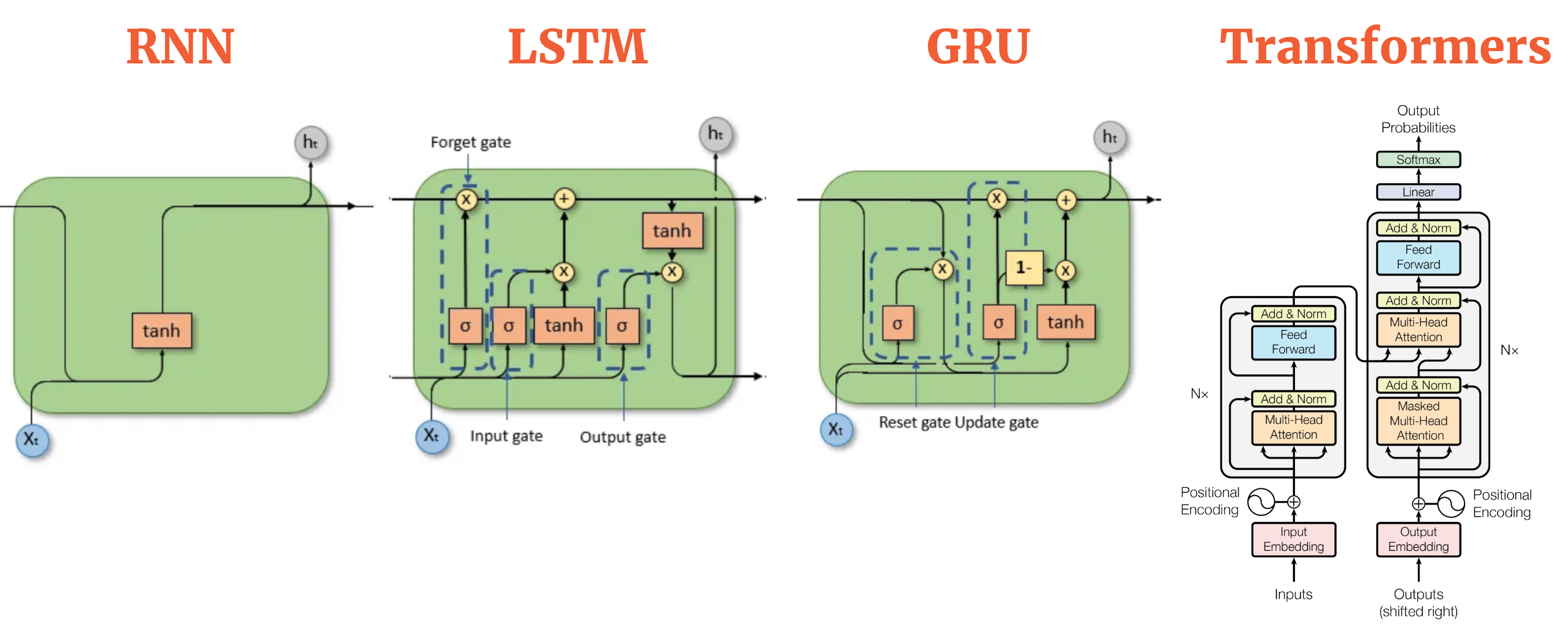
Source: Colah’s blog, and Attention paper. Compiled by AIML.com Research
RNN (Recurrent Neural Network), LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory), GRU (Gated Recurrent Unit) and Transformers are all types of neural networks designed to handle sequential data. However, they differ in their architecture and capabilities. Here’s a breakdown of the key differences between RNN, LSTM, GRU and Transformers:
[table id=23 /]
Comparing results of different models (from Scientific journals)
Included below are brief excerpts from scientific journals that provides a comparative analysis of different models. They offer an intuitive perspective on how model performance varies across various tasks.
- Transformer model for traffic flow forecasting with a comparative analysis to RNNs (LSTM and GRU) [Time Series problem]
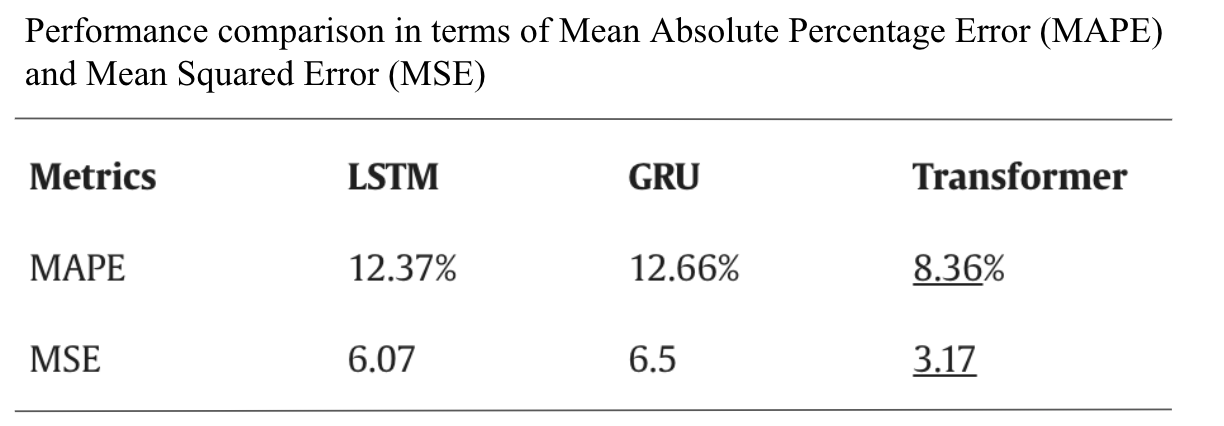
Source: Paper by Reza et.al, Universidade do Porto, Portugal
- RoBERTa-LSTM: A Hybrid Model for Sentiment Analysis With Transformer and Recurrent Neural Network [Text Classification problem]
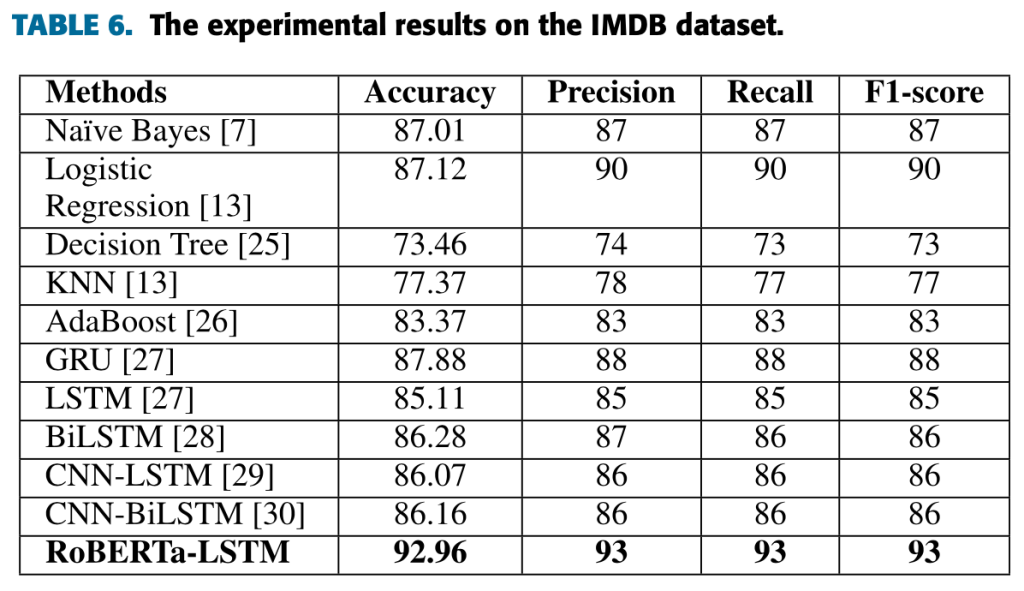
Source: Paper by Tan et. al., Multimedia University, Melaka, Malaysia
- Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training [Diverse: textual entailment, question answering, semantic similarity assessment, and document classification]
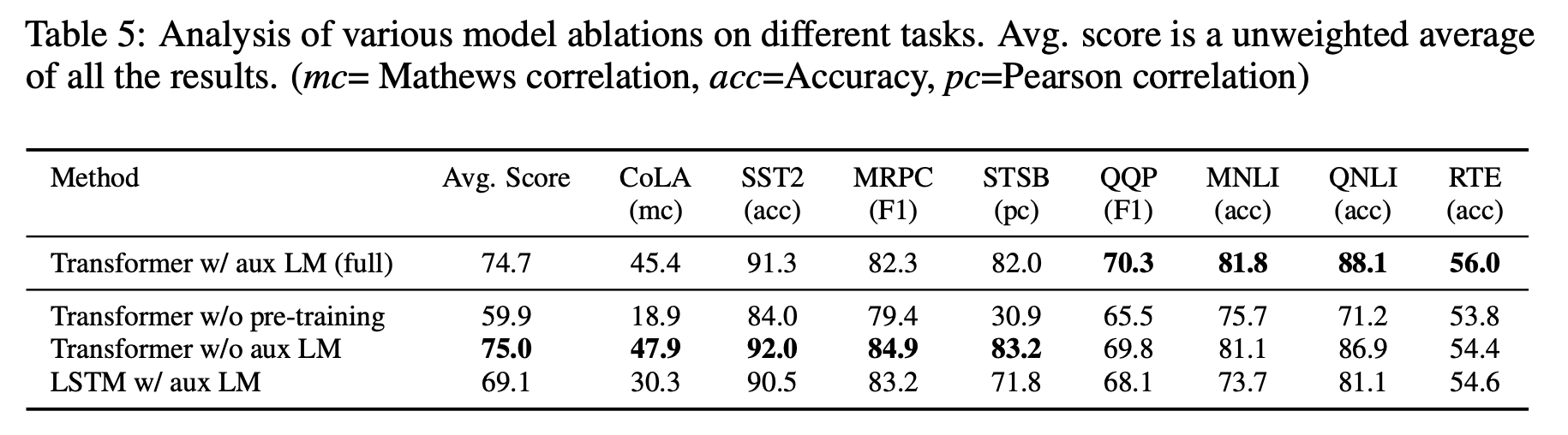
(CoLA, SST2, and others are a collection of datasets under the GLUE benchmark for evaluating Natural Language Systems)
Source: GPT paper by Radford et. al., Open AI
Conclusion
As shown above, while RNNs, LSTMs, and GRUs all operate on the principle of recurrence and sequential processing of data, Transformers introduce a new paradigm focusing on attention mechanisms to understand the context in data. Each model has its strengths and ideal applications, and you may choose the model depending upon the specific task, data, and available resources.
Video Explanation
- This video is part of the ‘Introduction to Deep Learning’ course at MIT. In this lecture, Professor Ava Amini delves into the concepts of Sequence modeling, and covers the full gamut of sequence models including RNN, LSTM and Transformers. This presentation offers valuable insights into the conceptual understanding, advantages, limitations and use cases of each model. (Runtime: 1 hr 2 mins)
- The second video is part of the ‘NLP with Deep Learning’ course offered by Stanford University. In this lecture, Dr. John Hewitt delivers a great explanation of the transition from Recurrent Models to Transformers, and a clear comparative analysis of the distinctions between the two. (Runtime: 1 hr 16 mins)
