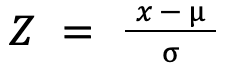A Z-score is a scaling technique performed in order to normalize the original data by subtracting the mean from each raw observation and dividing by the standard deviation. Basically, after transformation, the Z-score measures the distance of each observation from its mean, scaled by the standard deviation. In other words, a Z score of 0 means that observation has a value identical to the mean of the distribution, while a Z score of 1 implies that the observation is 1 standard deviation away from the mean.